1. Learning Outcome
1.1 Describe the roles an purposes
1.2 Compare the multidimensional nature with two-dimensional nature of database
1.3 Identify the importance of ensuring the cleanliness information
1.4 Explain the relationship between business intelligence and a data warehouse
2. Data Warehouse Fundamental
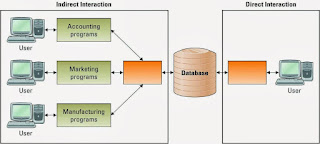
> Data warehouse - a logical collection of information
- gathered from many different operational database
- that supports business analysis activities and decision making tasks
> To aggregate information throughout on organization into a single repository for decision-making purposes
> Extraction, transformation, and loading (ETL) - a process that extracts information from internal and external database
- transforms the information using a common set of enterprise definitions
- load the information into a data warehouse
> Database contain information information in a series of two-dimensional tables
> Dimension- a particular attribute of information
- Once a cube of information is created, users can begin to slice and dice the cube to drill down into the information
- Users can analyse information in a number of different ways and with number of different dimensions
- Once a cube of information is created, users can begin to slice and dice the cube to drill down into the information
- Users can analyse information in a number of different ways and with number of different dimensions
2. Multidimensional Analysis and Data Mining
> Data mining - process of analyzing data to extract information not offered by the raw data alone
> To perform data mining users need data-mining tools
> Data-mining tools - uses a variety of techniques to find patterns and relationships in large volumes of information. Examples: retailers can use knowledge of these patterns to improve the placement of items in the layout of a mail-order catalogue page or Web page
3. Information Cleaning or Scrubbing
> An organization must maintain high-quality data in the data warehouse
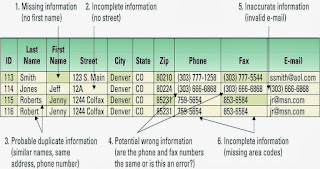
> Information cleansing or scrubbing – a process that weeds out and fixes or discards inconsistent, incorrect, or incomplete information
> Occur during ETL process and second on the information once if is in the data warehouse
Contact information in an operational system
Standardizing Customer name from Operational Systems
Information cleansing activities
Accurate and complete information
4. Business Intelligence
> Business intelligence – refers to applications and technologies that are used to gather, provide access, analyze data, and information to support decision making effort
> These systems will illustrate business intelligence in the areas of customer profiling, customer support, market research, market segmentation, product profitability, statistical analysis, and inventory and distribution analysis to name a few
> Eg: Excel, Access